
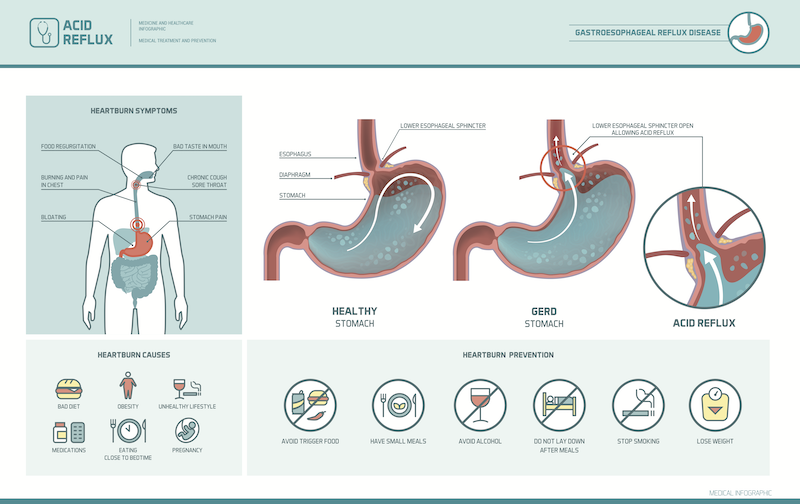
Typical symptoms in patients 50% of patients with GERD present with nonerosive reflux and normal endoscopic findings.Sliding hiatal hernia : ≥ 90% of patients with severe GERD.Gastrointestinal malformations and tumors: gastric outlet obstruction, gastric cardiac carcinoma.Inadequate esophageal protective factors (i.e., saliva, peristalsis).Smoking caffeine and alcohol consumption.Clearance can be disrupted by reduced salivation (e.g., due to smoking) and/or decreased peristalsis (e.g., due to inflammation ).Normally, acid reflux is neutralized by salivary bicarbonate and evacuated back to stomach via esophageal peristalsis.Anatomic abnormalities of gastroesophageal junction (e.g., hiatal hernia, tumors).Intragastric pressure is increased in pregnancy, delayed gastric emptying, and obesity, among other conditions.LES tone can be decreased by substances such as caffeine and nitroglycerin, as well as by conditions that cause denervation of the muscle layer, such as scleroderma (see “ Risk factors /associations ” below).Reflux occurs when the intragastric pressure is higher than that created by the LES.Imbalance between intragastric and lower esophageal sphincter ( LES ) pressures.About two-thirds of TLESRs are also accompanied by reflux of gastric content.Normally, TLESRs allow for the exit of accumulated gases, which distend the stomach.Increased frequency of transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxations ( TLESRs ).Gastroesophageal junction dysfunction can occur due to the following factors:.GERD develops when reflux-promoting factors, such as corrosiveness of the gastric juice, overcome protective mechanisms, such as the gastroesophageal junction and esophageal acid clearance.
Treating esophagitis is especially important because chronic mucosal damage can cause Barrett esophagus, a premalignant condition that can progress to adenocarcinoma. Management involves lifestyle modifications, medication, and, in some cases, surgery. Diagnostic studies, e.g., esophagogastroduodenoscopy ( EGD) and/or 24-hour pH test, may be indicated to confirm the diagnosis or to rule out other causes of symptoms.
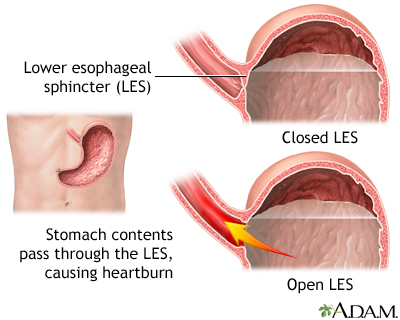
Most patients with suspected GERD should receive empirical treatment with proton pump inhibitors ( PPIs). Typical symptoms are retrosternal burning pain ( heartburn) and regurgitation, but the presentation is variable and may also include symptoms like chest pain and dysphagia. Risk factors include obesity, stress, certain eating habits (e.g., heavy meals or lying down shortly after eating), and changes in the anatomy of the esophagogastric junction (e.g., hiatal hernia). Reflux is primarily caused by an inappropriate, transient relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter ( LES). Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a chronic condition in which stomach contents flow back into the esophagus, causing irritation to the mucosa.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
